Introduction
Why do students hold a smartphone on their desk? This issue is becoming increasingly relevant as the widespread use of digital technologies leads to the blurring of the boundaries between virtual and real space, between study and entertainment. Students, having access to the Internet through their gadgets, can surf the web during lessons and not always for study purposes.
Researchers use the special term "cyberloafing" to refer to the use of technical devices (most often with access to the Internet) for personal purposes while studying or working. This is a special form of avoiding boring work or a variant of procrastination, carried out through the use of information technologies [Koay]. Researchers see cyberloafing as a type of counterproductive workplace behavior [Zhong]. However, cyberloafing can be seen not only in the workplace. It is observed in the academic environment too.
Scientists note that cyberloafing is a problem that has intensified due to the need to switch to a remote format of work or study, as well as the digitalization of education [Reizer].
The intensive development of digital technologies, their special role in the life of a modern person, and their widespread introduction into the learning system explain the growing interest of children in the use of digital technologies and the interest of teachers in assessing the advantages and risks of their use in education. Researchers from different countries conclude that information and communication technologies have become a natural part of education and learning [.Donham C, 2022; Deepa] and contribute to significant changes in the habitat and development of children [Sivrikova]. Digital games are increasingly included in classroom education in different countries around the world [Dubé]. For example, in 2019, 47% of teachers in grades 3–8 in the United States reported using digital games in their classrooms several times a week [Flynn]. Research in other countries also shows the use of digital tools in training as tools to transfer or strengthen academic skills [Luo, 2021]. The use of digital educational resources is now possible on a wide variety of media, including tablets, mobile phones, game consoles, portable game controllers, and computers [Flynn; Ricker]. Many of them have access to the Internet. Such innovations lead to the emergence of new forms of behavior in lessons, require a revision of the norms of "correct" childhood declared by psychology, and require the development of new methods for monitoring the behavior of children in the digital environment. However, solving such global problems requires a preliminary empirical study of the problem of media consumption among children. Firstly, new forms of deviant behavior, such as cyberloafing, deserve attention.
The request from society encourages researchers around the world to analyze the identified problem. Scientists analyze changes in the use of gadgets by children [Sivrikova], risks to the health, development, and education of children associated with the use of digital technologies [Flynn; Ricker], factors affecting academic performance and personal development [Margaretha; Mei, 2021; Moon, 2019], and teachers' willingness to digitally transform learning [Luo, 2021].
The reasons for the use of digital devices in the lesson are one of the central aspects of cyberloafing research. E. Ergun and A. Altun [Ergün, 2012] highlight the following causes of cyberloafing in the lesson: motivation, teacher personality, environment, and time. Other authors add to this list the content of the course, the student's identity, and their knowledge of information technology [25, 28]. When studying the personal predictors of student cyberloafing, the researchers found that this type of behavior in the lesson is influenced by psycho-social ideas, attitudes, and learning strategies [Wu, 2020; Wu]. Among the environmental factors associated with the level of cyberloafing of students are: level of study, family income, and place of residence [GökçearslanŞ,Uluyol Ç; Ugrin].
Researchers consider the positive and negative results of the digitalization of education. Data on the effects that are found with regard to academic performance are ambiguous, but in most studies, they are negative [Juuti]. Teachers admit that it is naive to expect schoolchildren to use digital devices exclusively for educational purposes during class. Moreover, this can negatively affect the emotional sphere of the child [Flynn; Ricker]. On the other hand, the researchers emphasize that interaction with digital technologies can displace educational content and other types of communication [Sailer, 2021].
A recognized fact is that the use of digital interactive technologies in the lesson leads to improvements in student motivation [Moiseeva, 2019], metacognition [Ricker], stress reduction, mood improvement, self-development, and multitasking ability [9, 6].
The ability to multitask is higher in representatives of those generations who were born in the era of intensive development of Internet technologies, and cyberloafing does not negatively affect the cognitive activity of generation Z [Mihelič, 2022]. Researchers recognize the possibilities of cyberloafing as a means of restoring effort [27, 24].
It should be noted that all the empirical data obtained on the prevalence of cyberloafing among students was obtained by foreign researchers. In Russia, such studies have not yet been carried out. In this regard, the issue of studying the level of cyberloafing among Russian students and schoolchildren is relevant.
Methodology
Study flow chart. Students and schoolchildren took a voluntary, anonymous part in the study of the peculiarities of media consumption. To do this, they filled out specially prepared forms with a cyber buffer scale and brief information about them (age and gender).
Study sample. The study involved 233 respondents (ages 13 to 20). 146 schoolchildren aged 13–15 years (42% boys and 58% girls) and 87 students aged 17–20 (40% male and 60% female). The survey took place in classrooms during extracurricular hours. Participation was voluntary.
Research methods
We used the cyberloafing scale proposed by Y. Akbulut et al., adapted by N.V. Sivrikova [Moiseeva, 2019], to collect empirical data. The scale contains 24 points (for example, I view my friends' posts). Previously, the study participants were given instructions: Below are a number of statements that relate to the use of the Internet during classes (lessons) for personal purposes (not to solve the tasks set by the teacher). Each of them may be more or less relevant for you. Evaluate the following behaviors: Use a five-point scale for this: 1-never, 2-rarely, 3-sometimes, 4-often, and 5-constantly.The questionnaire included questions about gender, year of birth, and the digital devices available to the study participants.
The methodology is based on a five-factor cyberloafing model. It allows you to estimate the frequency of five forms of cyberloafing behavior. These are online shopping (6 points), online content usage (7 points), games (3 points), online sharing (9 points), and communication on social networks (5 points). Reliability indicators (Kronbach α value) of individual sub-scales ranged from 0.78 to 0.88.
The analysis of the data assumed an assessment of the distribution parameters of the studied features in the sample (Table 1).
Table 1. Parameters of distribution of studied cyberloafing features
|
cyberloafing behavior |
Levene's test |
М |
SD |
Asymmetry |
Excess |
|
|
|
|
F |
P |
|
|
|||||
|
sharing |
10,7 |
0,001 |
2,6 |
1 |
-0,4 |
0,2 |
||
|
shopping |
6,5 |
0,011 |
2 |
1,1 |
0,5 |
-0,5 |
||
|
content usage |
11,7 |
0,001 |
2,7 |
1,1 |
-0,5 |
-0,1 |
||
|
games |
0,5 |
0,5 |
1,7 |
1 |
1,1 |
1,7 |
||
|
communication on social networks |
3,3 |
0,1 |
2,4 |
1,2 |
0,1 |
-0,6 |
||
Empirical distribution parameters differ from normal distribution parameters. According to Levеne's criterion of Equality of Variances, the application of parametric processing methods to the resulting array of empirical data will be incorrect. Therefore, we used the Mann-Whitney U test to compare the level of cyberloafing in schoolchildren and students (as well as in respondents of different genders). We used Statistical Software Package (SPSS) version 23.0 to perform the calculations.
Study results
The survey results showed that the study participants most often own a smartphone (86%). About half of them (58%) own a laptop, about a third (29%) own a stationary computer, and about a quarter (26%) own a mobile phone. Thus, it turned out that smartphones were the most popular among the study participants.
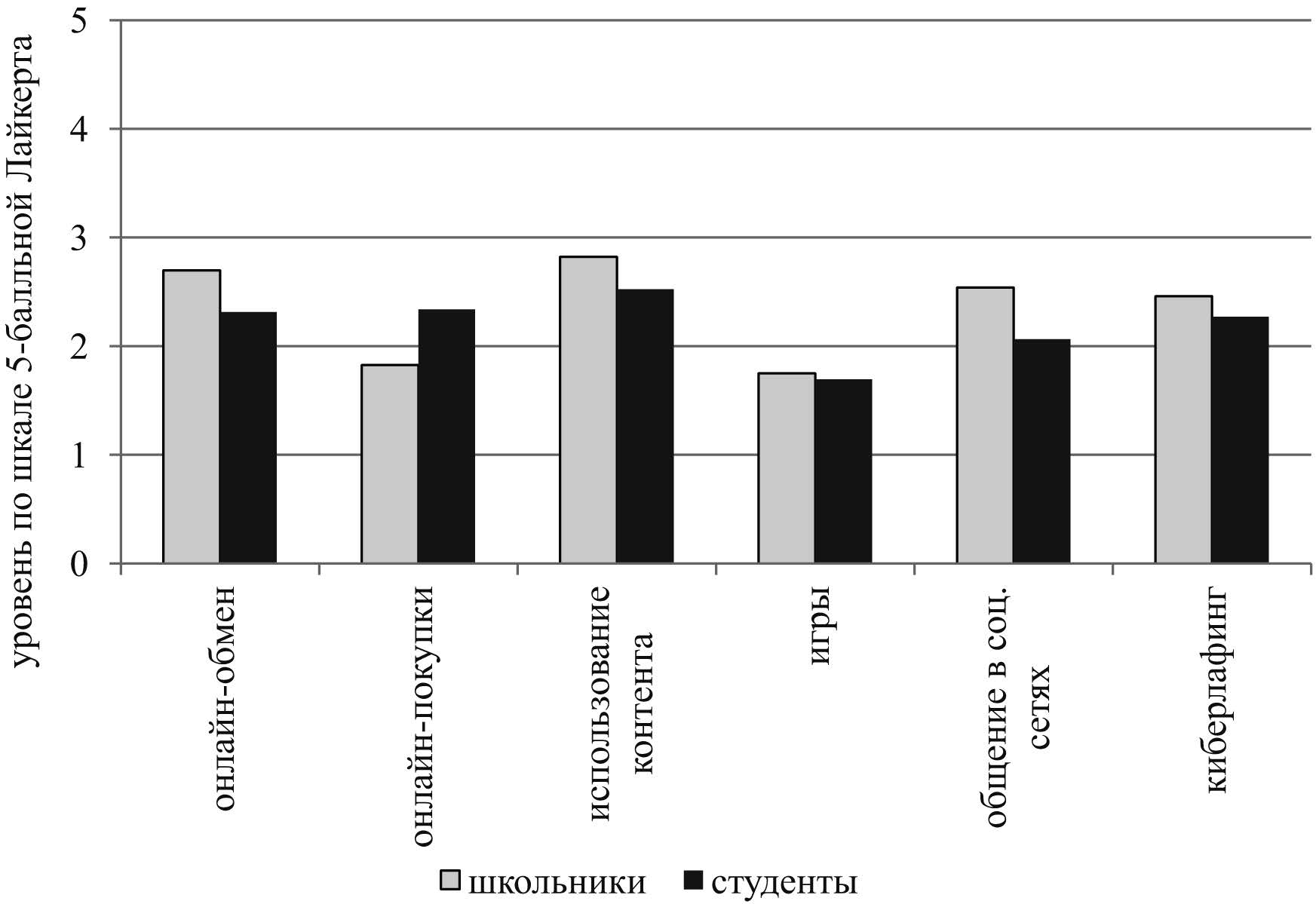
The figure shows the results of the analysis of mean values by sample, which reflect the severity of individual cyberloafing factors among the study participants. The findings say that students and schoolchildren use the Internet during study sessions for non-study purposes, rarely or sometimes. Most often, during lessons, study participants use the Internet to search for information. During training sessions, they play digital games. These features are typical for both schoolchildren and students (Fig.).
Fig. Features of cyberloafing among schoolchildren and students
We applied the Mann-Whitney U test to analyze differences between study participants at different learning stages (Table 2).
Table 2 Differences in the level of cyberloafing in students and schoolchildren
|
cyberloafing behavior |
N |
mean rank |
U |
p |
|
||
|
sharing |
schoolchildren |
146 |
125,18 |
5157,0 |
0,02 |
||
|
students |
87 |
103,28 |
|||||
|
shopping |
schoolchildren |
146 |
103,17 |
4332,5 |
0,00005 |
||
|
students |
87 |
140,20 |
|||||
|
content usage |
schoolchildren |
146 |
121,93 |
5631,5 |
0,15 |
||
|
students |
87 |
108,73 |
|||||
|
communication on social networks |
schoolchildren |
146 |
115,79 |
6174,0 |
0,72 |
||
|
students |
87 |
119,03 |
|||||
|
games |
schoolchildren |
146 |
127,17 |
4865,5 |
0,003 |
||
|
students |
87 |
99,93 |
|||||
|
cyberloafing |
schoolchildren |
146 |
119,22 |
6026,5 |
0,51 |
||
|
students |
87 |
113,27 |
|||||
Analysis of the differences between the compared groups showed that the frequency of use of such forms of cyberloafing as exchange, online shopping, and use of social networks is associated with the stage of training. In particular, students more often than schoolchildren make online purchases during study sessions. This may be due to their greater material independence. Perhaps they shop more often than schoolchildren, since some of them live separately from their parents. In addition, shopping via the Internet is not always possible for minors. Schoolchildren are more likely than students during study sessions to communicate on social networks and share information online. This pattern may be related to the differences in tasks and leading activities among schoolchildren and students. The leading activity of the former is communication with peers, which in recent years has become more dependent on digital means of communication. An important task of adolescence is self-expression and self-assertion through the expression of one's opinion. This is probably why teenagers are more dependent on various forms of sharing on the network: likes, comments, etc.
In Table 3, we presented data reflecting the differences in cyberloafing due to the gender of respondents.
Table 3. Features of cyberloafing in respondents of different sexes
|
cyberloafing behavior |
N |
mean rank |
U |
p |
|
|
|
sharing |
male |
97 |
110,94 |
6008,0 |
0,25 |
|
|
female |
126 |
121,32 |
||||
|
shopping |
male |
97 |
115,49 |
6450,0 |
0,77 |
|
|
female |
126 |
118,07 |
||||
|
content usage |
male |
97 |
125,91 |
5731,5 |
0,09 |
|
|
female |
126 |
110,64 |
||||
|
communication on social networks |
male |
97 |
137,39 |
4618,0 |
0,0001 |
|
|
female |
126 |
102,46 |
||||
|
games |
male |
97 |
107,75 |
5698,5 |
0,05 |
|
|
female |
126 |
123,60 |
||||
|
cyberloafing |
male |
97 |
119,61 |
6343,0 |
0,62 |
|
|
female |
126 |
115,14 |
||||
Boys are more likely than girls to play digital games during training sessions. Girls are more likely than boys to use social media during training sessions.
Discussion
As a result of comparing the data obtained with the data of other studies, we concluded that among Russian schoolchildren and students, the phenomenon of cyberloafing is less common than among schoolchildren in other countries. The reason can be in the policy of banning gadgets in a Russian school (although it should be noted that recently they are increasingly moving away from it). This practice indicates that cyberloafing is seen as a barrier to the successful integration of information and communication technologies into the educational environment.
In the presented study, the level of cyberloafing in schoolchildren indicates that they rarely or sometimes use the Internet during lessons to solve problems unrelated to learning. Similar data on the prevalence of cyberloafing was found in samples of students from Turkey [F. G.] and Turkish students in grades 6–8 [Tanrıverdi]. On the other hand, students in the USA [Sharma] and Indonesia [Margaretha] demonstrate cyberloafing just sometimes.
As a result of comparing the popularity of certain types of cyberlafing, we found that schoolchildren in classes use access to online content to solve the problems of socialization (self-expression and maintaining significant relationships), students also purchase goods during the lessons. According to other researchers, students communicate more often during classes via the Internet [Metin-Orta]. Such differences may be related to cultural aspects.
There is conflicting data on gender-related differences in cyberloafing studies. In some studies, scientists found no difference in the level of cyberloafing among people of different genders [22, 28] or no association between gender and cyberloafing [Mei, 2021]. In other studies, it was found that gender mediates the relationship between attitude-behavior and goal-behavior [Metin-Orta], which should also manifest itself in the features of cyberloafing. Therefore, it can be assumed that the reason for the inability to detect gender differences in the level of cyberloafing is related to the features of the study sample or to the features of the applied data analysis strategies.
In a number of studies, the authors say that men more often demonstrate cyberloafing than women, both in workplaces and in educational institutions [.Donham C, 2022; Toker]. Researchers attribute this to gender differences in the use of the Internet. For example, the number of male Internet users exceeds the number of female users in Turkey [F. G.]. In Russia, the distribution of Internet users is also shifted towards men (53.5% versus 46.5%) compared to the natural distribution of the population. It is expected that men will transfer the habit of using the Internet to their place of work or study.
Gender differences in the use of the Internet and cyberspace can be controversial. For example, they can vary depending on the type of cyberloafing, which was confirmed in our study. Gender differences in cyberloafing can be influenced by different factors. This is the nature of the study sample and control variables, such as social desirability [Metin-Orta]. Our study found that girls more likely than boys visit social media during lessons, and boys more likely than girls play games. These differences can be explained by the fact that psychological features related to gender determine the general activity of a person [Moiseeva, 2019].
Conclusion
The study contributes to the study of new forms of deviant interleaving (cyberloafing). Its value is increasing due to the active introduction of remote formats of learning using communication technologies in the educational process. By the results we received we can conclude that in Russia, the phenomenon of cyberloafing is less common than in other countries. But this form of behavior is already observed in schools and institutions of higher levels. An analysis of the experiences of other countries shows, that further monitoring of the level of cyberloafing in Russian educational institutions is necessary. It is also necessary to study this phenomenon and develop measures to prevent its negative effects.