Introduction
The aging population currently constitutes seven percent of the world’s population, and the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates it will reach 11 percent of the world's population by 2050 [Ageing and health, 2022]. The prevalence of some mental illnesses is higher in old age; therefore, it disrupts the independence of old people and reduces their quality of life [Stenholm, 2015].
Depression is one of the most important prevalent mental disorders among older adults [Axmon, 2018]. It is estimated that 13.3 percent of the elderly above the age of 60 suffer from depression [Van Damme, 2018]. Depression is recognized as the most debilitating psychiatric illness [Padayachey, 2017]. Disability-adjusted life years (DALY) rate of depression is higher in old age than in other ages [Ogbo, 2018]. The disability-adjusted life year (DALY) is the number of years lost due to ill health or disability [Cao, 2019]. The cost of treatment for old patients with depression is 1.86 times higher than for other old patients [Van Damme, 2018]. So this issue also imposes huge economic burdens on the healthcare systems [Stenholm, 2015]. Depression is determined by signs and symptoms such as anhedonia (getting no pleasure from previously pleasurable activities) and low mood most of the time in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition (DSM-5). One of these signs in the elderly along with experiencing four or more issues such as significant loss or increase of weight or appetite, insomnia or oversleeping, fatigue, psychomotor or slowness disorder, decreased ability to concentrate and make decisions, feelings of guilt or worthlessness, and thoughts of death or suicidal ideation, for more than two consecutive weeks leads to the diagnosis of depression [Diagnostic and Statisctical, 2013]. Nevertheless, some other symptoms may indicate depression in the elderly. For instance, unexplained physical pain, fatigue, back pain, a headache, decreased libido, or chest pain [Haigh, 2018]. It is worth noting that the underlying mechanisms of depression and dysfunction are dynamically and progressively related to each other, meaning that the exacerbation of one of them leads to the intensification of the other one as well [Remes, 2021]. Furthermore, depression results in physical and emotional damage, decreased quality of life, economic problems, and an increased possibility of mortality [Akosile, 2018].
Various treatments have been approved for depression in older adults. Overall, the existing treatments can be divided into two pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical categories. The most common pharmaceutical treatment for the depression of old patients is using serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and old-generation drugs (e.g. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors and Tricyclic Antidepressants) are used less in elderly patients due to their side effects [Kekic, 2016]. Aging can impose other limitations on medication treatments by altering the function of psychiatric drugs, which can lead to reducing the effect of the drug and the increasing possibility of drug-drug interactions [Gálvez, 2015]. Meanwhile, the use of non-pharmacological treatments with or without drug treatment can have fewer side effects and may also accelerate the improvement of depression symptoms.
The non-pharmaceutical treatments include cognitive-behavioral therapy, group therapy, family therapy, and phototherapy [Gartlehner, 2017]. Another proposed treatment for depression is the modulation of brain activity using brain stimulation techniques, which has been approved in adults [Kekic, 2016]. The most common brain activity modulation methods include electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) [Gálvez, 2015]. TDCS is a device for electrical stimulation of specific areas of the brain and a non-invasive neural stimulation method that causes changes in the patterns of brain activity associated with the symptoms of depressive disorder [Li M.-S, 2019]. Recent studies suggest that TDCS has long-lasting neuroplasticity effects; the activity of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) is decreased in depression, and it is hypothesized that TDCS can increase the activity of this region [Brunoni, 2013]. The effectiveness of TDCS in the treatment of mental disorders such as adult depression, schizophrenia, substance abuse, obsessive-compulsive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and anorexia nervosa has been confirmed [Kekic, 2016; Tortella, 2015]. Few studies have been conducted on the effect of TDCS and the results are not clear. The systematic review found that the data do not support the use of TDCS as an add-on treatment and that further studies are needed [Meron, 2015]. This study hypothesizes that Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) has an effect on depression in older adults.
Materials and methods
Study design and participants
This study is an unblinded randomized controlled trial (neither the patient, the researcher nor the rater). We selected samples from older adults referred to the clinics of geriatrics and geriatric psychiatry in Hazrat Rasul Akram Hospital in Tehran (October 2018 to April 2019). We considered 30 participants for each group.
We planned to include 90 old patients in the study (45 people in each group), but the sampling remained incomplete due to the outbreak of COVID-19. We selected 60 old patients who met the inclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria were age above 60 years and a Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) score above 9. The exclusion criteria were previous history of mental disorders and antidepressant therapy and psychotherapy in the medical record or self-report, the presence of metals in the body, and a history of sensitivity to TDCS or contraindications for TDCS (e.g. history of heart arrhythmia, cardiac pacemaker, and strokes).
Intervention
We randomly allocated these 60 participants to the control and intervention groups (30 old people in the control group and 30 old people in the intervention group). We performed random allocation with random permutations via online software. The participants took pre-test and post-tests before, during, and after the intervention. The intervention took place under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment was already prepared at the study site. Sixty participants were included in the study and no participants dropped out. In the intervention group, the treatment was initiated with a 25 mg dose of sertraline on the first day, which increased to 50 mg per day after a week. The therapy with TDCS was also applied along with the pharmaceutical treatment. We used the OASIS PRO device made by Mind Alive Company (The size of the electrodes: 7cm × 5cm). TDCS was carried out once a day for five days. Each session lasted 20 minutes and was performed with a 2 mA current anode electrode at F3 and a supraorbital cathode at Fp2. The red dot is the anode in the left DLPFC (F3) while the blue dot is the cathode in the contralateral supraorbital region (Fp2) (fig. 1) [Li M.-S, 2019]. The control group received only sertraline with the same dose. This study was in line with the CONSORT guideline. The post-test was repeated in the patients after the third and fifth sessions of TDCS therapy and one month after the last session (fig. 2).
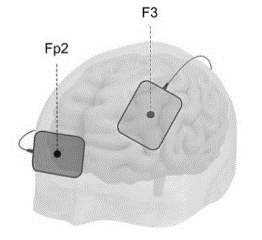
Fig. 1. Electrode placement [Lema, 2021].
Measurements
Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS)
GDS is applied to screen depression in older adults. We used the 15-item version. The scale was implemented for 10–15 minutes. The highest possible depression score is 15, and high scores show the severity of depression. A score of 0–4 shows a lack of depression, whereas the scores range from 5–8, 9–11, and 12–15 demonstrate mild, moderate, and severe depression, respectively. The validity of the scale was determined by Yesavage et al. (1983), where internal consistency and the reliability coefficient were estimated at 0.94 and 85%. Moreover, the criterion validity of the scale was calculated, and the correlation between GDS and Zong Depression Scale and the Hamilton Depression Scale was 0.84 and 0.83, respectively. The study of psychometric properties of the Persian version of GDS has been done and approved [Malakouti, 2006].
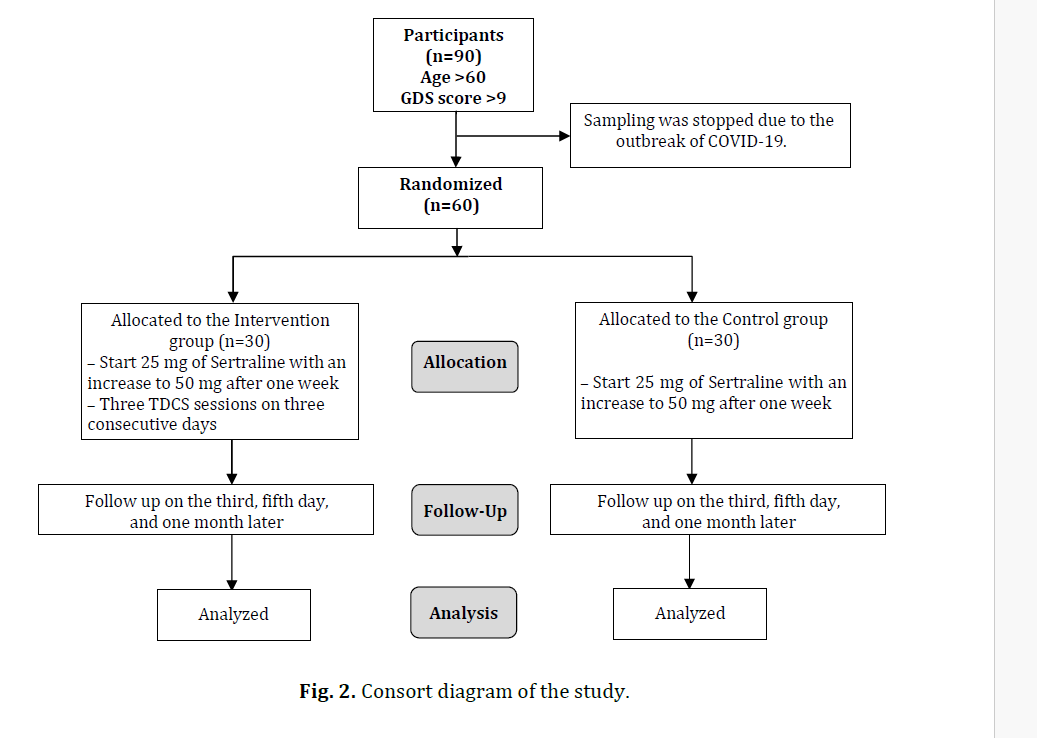
Fig. 2. Consort diagram of the study.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed via SPSS v. 22 software and statistical methods were used for each of the following objectives. The objectives of this study include:
- Determining and comparing the mean and standard deviation GDS in the control and intervention groups. We used descriptive statistics, chi-square, independent t-tests, and ANOVA tests.
- Comparison of the two groups over time was done with t-test and repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 72.01±6.71 years. The participants were 40% female (Table 1). Demographic variables in the two groups do not affect the pretest (sex: p=0.94, education: p=0.98, and marital status: p=0.55).
Table 1. Comparison of demographic variables in control and intervention groups
|
|
Control Groups |
Intervention Groups |
P-value |
|
|
Age |
71.13 ± 5.71 |
72.86 ± 7.72 |
0.49 |
|
|
Sex |
Male |
16 |
20 |
0.71 |
|
Female |
14 |
10 |
||
|
Education |
Illiterate or primary school |
16 |
14 |
0.97 |
|
Middle school |
6 |
6 |
||
|
High school |
6 |
8 |
||
|
University |
2 |
2 |
||
|
Marital status |
Single |
10 |
16 |
0.46 |
|
Married |
20 |
14 |
||
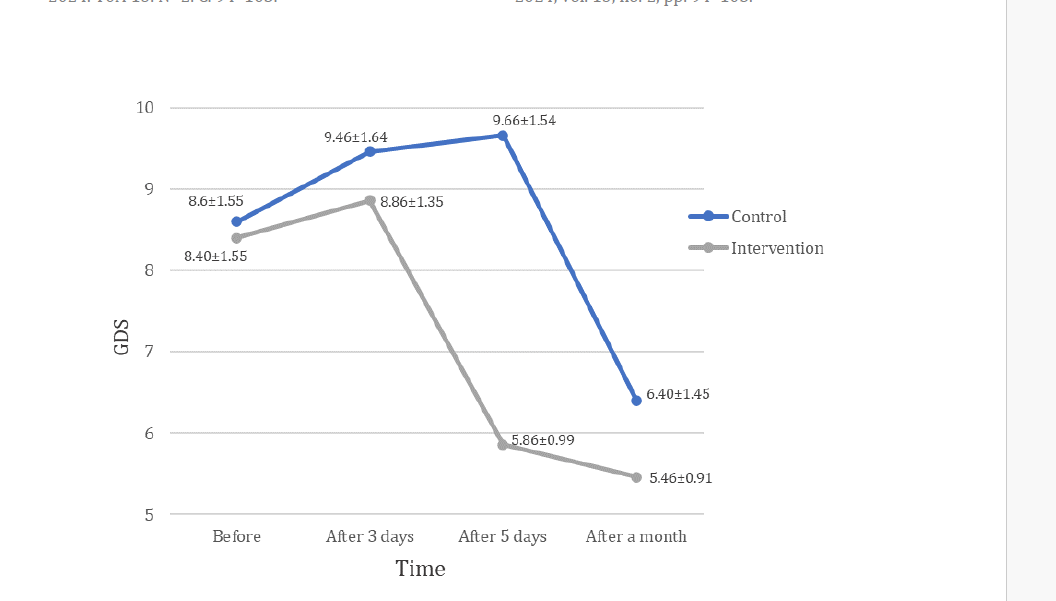
The comparison of the mean GDS score did not show a significant difference between the two groups before intervention (p=0.73) and after 3 days (p=0.28). The GDS score had a significant decrease in the follow-up on the fifth day and one month later (p<0.001). There was a significant difference between the two groups (p5th day<0.001 and pone month later=0.03) (Table 2). Figure 3 shows the changes in GDS scores in two groups.
Table 2. Comparison of Geriatric Depression Scale in control and intervention groups
|
|
Control Groups (M ± SD) |
Intervention Groups (M ± SD) |
Levene's Test |
P-value |
|
Before study |
8.4 ± 1.53 |
8.4 ± 1.57 |
0.92 |
0.73 |
|
After 3 days |
9.47 ± 1.64 |
8.87 ± 1.33 |
0.52 |
0.28 |
|
After 5 days |
9.66 ± 1.54 |
5.86 ± 0.97 |
0.05 |
<0.001 |
|
After a month |
6.42 ± 1.45 |
5.48 ± 0.92 |
0.09 |
0.03 |
|
Mauchly's Test of Sphericity |
Mauchly's W=0.59 Df=5 p=0.01 |
|||
|
Tests of Within-Subjects Effects |
Greenhouse-Geisser=0.74 Df=2.24 F=103.79 p<0.001 |
|||
Fig. 3. Changes in GDS scores during the study in the control and intervention groups.
Discussion
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) on depression in older adults. The results show that the decrease in GDS score started earlier in the intervention group than in the control group. A course of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) can significantly reduce depression scores in old patients.
There was a significant difference between the mean scores of depression in the screening of the electrical stimulation group compared to the control group during one month, i.e. the improvement of GDS score in the first group started faster, and finally, the improvement in this group was better than the second group after one month, but in the fifth session, the GDS score in the intervention group compared to the control group showed a significant decrease (p<0.001), with final results. The results of this study showed that the use of TDCS has a significant effect on the improvement of depression in the elderly and this effect continues until the follow-up stage. This is consistent with the research of Kumar et al (2020) on the effect of TDCS on adult depression [Rajji, 2020]. It is stated that tDCS can increase or decrease the effect of pharmacological interventions [Stagg, 2011]. Brunoni et al. also found that the combination of pharmaceutical treatment and TDCS could be more effective than pharmaceutical treatment alone [Brunoni, 2013].
To explain this finding we can say that TDCS is a therapeutic strategy that allows non-invasive treatment in the elderly. It is used in the treatment of psychiatric diseases by increasing the excitability and plasticity of the cerebral cortex. This intervention stimulates and increases the activity of brain cells by delivering electrical signals. The way that the stimulation changes brain function is either by causing the neuron's resting membrane potential to depolarize or hyperpolarize [Xia, 2020]. Patients underwent 20 min TDCS sessions with 2 mA current and anode electrode at F3 and a supernatant (Fp2). In addition, this device is small, portable, inexpensive, and has few side effects. In this study, the complications were brief and rare and had the same distribution in the group receiving the stimulus.
The present study showed that the onset of effect and durability of the TDCS effect is better than treatment with sertraline alone. Rigonatti et al. found that TDCS therapy can lead to faster improvement compared to pharmaceutical treatment [Rigonatti, 2008]. Loo et al. also obtained similar results to the present study [Loo, 2018]. It has been found that TDCS has a positive effect on the working memory and depressive symptoms of depressed patients [Palm, 2016]. According to the findings of this study, it is better to start pharmaceutical treatment with TDCS together so that the patient can benefit from both treatments.
Conclusion
The results suggest that Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) can reduce depression along with medication therapy, more studies are needed, such as longer duration and with more people.
Limitations and suggestions
The sample size of this study was small, which was due to the caution in the selection of participants, the limited time of the study, and the outbreak of COVID-19. This study is an open-label study without any sham-controlled groups. Furthermore, this study included the age above 60 years and the Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) score above 8 only. This means that only depressive symptoms were assessed by using a subjective scale. Therefore, some participants may not be patients with depression. We did not use a sham, considering that the intervention and control groups were not related.