The basic tenets of the theory of J. Piaget[Davydov, 1998]. The scientific school of J. Piaget considers the formation of intelligence as the pivotal line in the mental development of a child, which determines the development of all other mental processes. According to J. Piaget, the qualitative uniqueness of each stage of cognitive development, as well as leaps and transitions, made from one age level to another, are all determined by the in-life formation of structures of intellectual activity, which are age-specific.
The fundamental idea of development in the theory of J. Piaget consists in the fact that intellectual operations are carried out in the form of integral structures. These structures are formed due to the equilibrium, which the general development of intelligence strives to achieve. The Geneva School of Genetic Psychology, created by J. Piaget and his followers, studies cognitive development of the child, and, in fact, the origin of intelligence. The main task of this scientific school is studying children’s concepts about natural phenomena, describing peculiarities of children’s logic and, as a result, substantiation of the mechanisms of cognitive activity in general. The fundamental answers, found in J. Piaget’s works regarding the development of the operational structures of children’s thinking, constitute the core of the Geneva scientific school.
In general terms the basic tenets of the theory of J. Piaget can be formulated with the help of these four axioms:
1. Intelligence is constructed on the basis of action.
2. Action is the source of development.
3. Thought is a condensed form of action.
4. Cognition at all genetic levels is a product of real actions performed by the agent (subject) with objects.
While substantiating these ideas, Piaget proceeded from the fact that the object(s) exist(s) independently of the agent. In order to acquire knowledge about the objects, the agent must act with them: bind, separate, move, change, combine, i.e. transform them. Development takes place on the basis of real actions performed by the agent with the objects of the external world. Moreover, the description of the agent’s interaction with the object cannot be completely captured by the formula S^R (unidirectional arrow). From Piaget’s perspective, the essence of subject-object interactions is most fully represented in the formula S→R (reversible arrow), which captures the reversible character of this relationship.
The content of the agent’s interactions with objects and the reversible character of these relationships reflect Piaget’s ideas about transformation and construction. Thus, the idea of transformation indicates the fact that the boundary between the agent and the object is not established from the very beginning, and that in every action the subject and the object are mixed. The idea of construction presupposes that objective knowledge is subordinate to certain structures of action. Moreover, the structures of action are given neither in the objects, nor in the agent, since the agent must learn to coordinate their actions.
The most general content, which is preserved in the action, is characterized by a scheme of action, which, according to J. Piaget, is a structure at a certain level of cognitive development, and in a narrow sense, a sensorimotor element of the concept. Relying on the concept of the scheme of action, Piaget introduces a fundamental difference between the form and the content of cognition. In his theory, the content of children’s cognition represents something, which is acquired through experience and observation, while the form of cognition is the “general scheme” of the agent’s thinking activity, in which the agent’s interactions with the objects are included. It is not the object per se that plays the main role in the process of cognition: the agent him or herself chooses the object depending on the level of the development of intellectual structures. Thus, the process of cognition (“acquiring knowledge” about the reality) depends on the development of intellectual structures.
J. Piaget describes three main forms of experience that determine the development of intellectual structures [Piaget, 2001]:
• Experience-exercise that is important for building a skill.
• Physical experience, due to which the child, while interacting with objects, begins to distinguish the physical properties of objects (shape, weight, volume, area, etc.).
• Logical and mathematical experience elicited by a child from the actions with objects. It is characterized not only by the orientation on a pragmatic result, but also on the means of action itself, which constitutes a necessary condition for the development of intelligence. Logical and mathematical experience is crucial for the development of intelligence and designates a higher level of mental development.
The law of intellectual development in the theory of J. Piaget. One of the main discoveries of J. Piaget is the discovery of the egocentrism of children’s thinking. According to Piaget, egocentrism is the main feature of thinking, a hidden intellectual position, which reflects the peculiarities of children’s logic, children’s speech and children’s vision of the world. In numerous research works, conducted in the framework of Piaget’s scientific school, egocentrism is defined as a kind of systematic and unconscious illusion of cognition, as a form of the initial centering of the mind, which characterizes mental activity in its origin. Egocentrism points to the fact that the external world does not directly affect the agent’s mind, and that our knowledge of the world is neither a copy, nor a simple display of external events.
The basic law of mental development in the theory of J. Piaget is the law of decentration, the law of transition from general egocentricity to intellectual decentration, which is expressed in the child’s transition from egocentrism to an objective position in acquiring knowledge about things, other people and him/herself. Importantly, according to J. Piaget, the key provision that determines the essence of the law stated above, is that the transition from egocentric to an objective position underlies the process of socialization, that is, the transition from the individually subjective to the social. J. Piaget believes that the thought is formed on the basis of action, but the source of integral logical structures (the development of individual intelligence) should be sought in the socialization of the individual [Piaget, 1960], [Piaget, 2001a].
In the theory of J. Piaget socialization is regarded as a process of adaptation to the social environment, consisting in the fact that a child, who has reached a certain level of intellectual development, becomes able to cooperate with other people, because he or she already distinguishes his or her own point of view and coordinates it with those of other people. Social life starts playing a progressive role in the development of the mind only at those stages, when relations of cooperation develop, as well as debates and discussions with peers emerge. This turning point in development takes place at the age of around 7—8 years. Before this age, the leading role in a child’s development belongs to the relations with adults, which, as J. Piaget emphasizes, are built primarily on the basis of unilateral respect and authority of the adult.
According to J. Piaget, “at the pre-operational levels, extending from the appearance of language to the age of about 7—8 years, the structures associated with the beginnings of thought preclude the formation of the co-operative social functions which are indispensable for logic to be formed. Oscillating between distorting egocentricity and passive acceptance of intellectual suggestion, the child is, therefore, not yet subject to a socialization of intelligence which could profoundly modify its mechanism” [Piaget, 1960, p. 162]. Therefore, it is precisely at the stage of the formation of concrete operations that the problem of correlation between the influence of social exchange and the impact of individual structures on the development of thinking arises in acute form.
Revealing the content of the process of socialization, Piaget points out, that while interacting with adults and peers, children aged 7—8 years experience a socio- cognitive conflict, when the point of view of other people becomes significant and needs to be taken into account as children perform their own actions. The point of view of the other is correlated with the child’s position, and is taken into account and included in the process of constructing an action; it is fixed in the emerging scheme of the action, and becomes a condition for the development of the emerging groupings (Fig. 1).
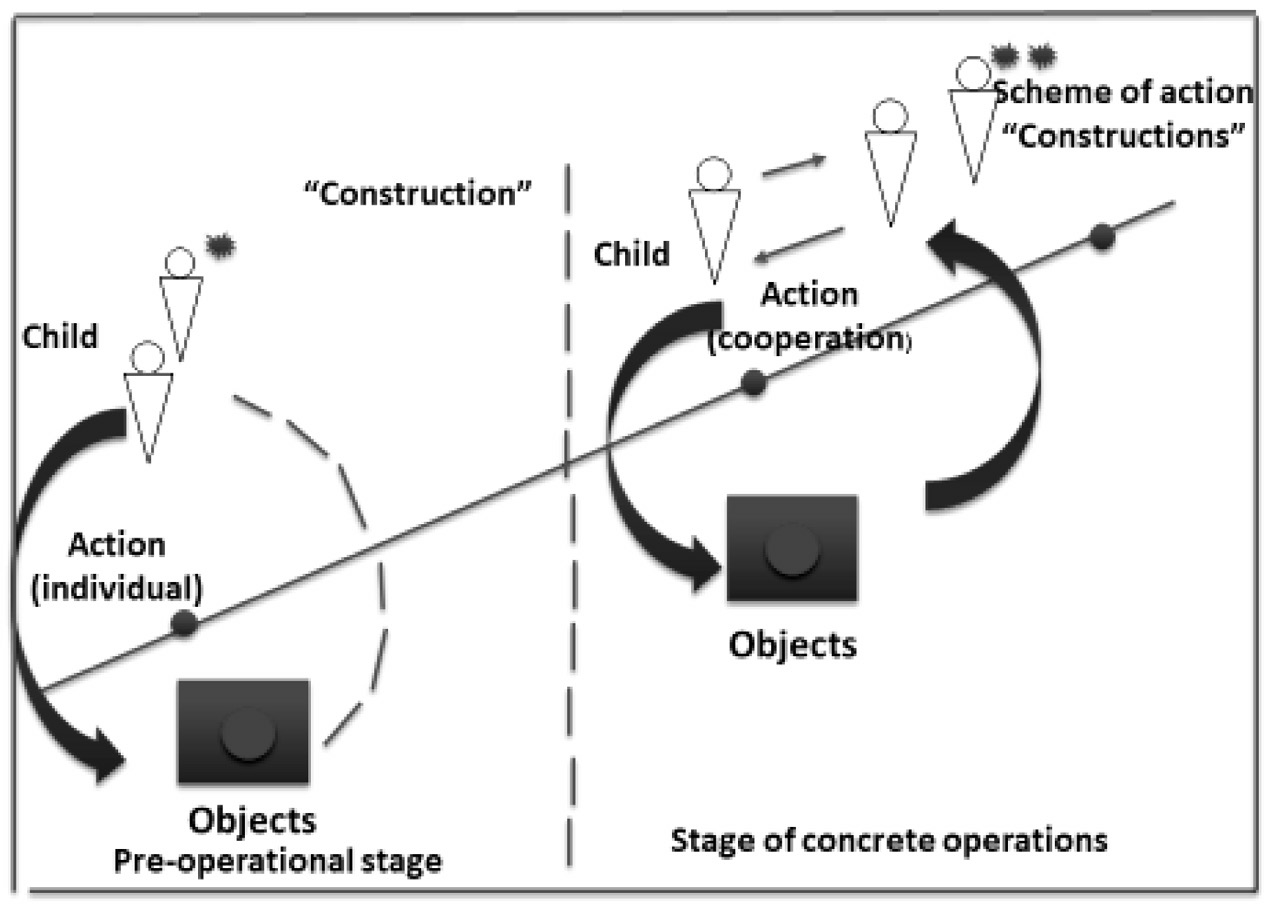
Fig. 1. Socio-cognitive conflict as a mechanism of development of individual intelligence in the situation of cooperation (an asterisk indicates the acts of reflection that emerge during the execution of an action as described by J. Piaget:
* — reflection on the properties of object
** — reflection on the means of action)
In the theory of J. Piaget, the isomorphism of operational structures and structures of cooperation is considered as a consequence of the more general law of the development of groupings. According to Piaget, each grouping, internal for an individual, is a system of operations carried out jointly, that is, in the proper sense, cooperation. This form of equilibrium is not the result of solitary intellectual thinking. Internal operational activity and external cooperation represent two corresponding processes, and the equilibrium of the one depends on the equilibrium of the other.
Intellectual development in the context of social interactions in the theory of J. Piaget. The analysis makes it possible to articulate the general principles of cognitive development in the theory of J. Piaget, emphasizing the special role that social interactions play in this process. According to J. Piaget:
1. The basis of human intellectual development (the development of thinking) is a qualitative change in the forms of experience, based on the performance of one’sownactions.
2. The means of performing individual actions in the conditions of S→←O interactions are the emerging structures (“knowledge” about the object and the structures of action subordinate to it).
3. The invariants of action (reflected experience) take shape of action schemes (an action scheme is a structure at a certain level of mental development, a mental system or integrity, whose principles of activity are different from those of the activity of its parts).
4. Cooperation (collaboration) allows to fulfill the correct transfer of a concept, starting from the stage of concrete operations. The condition for such a transfer is a socio-cognitive conflict — a new type of relationships between agents, that replaces the relationships of prestige and authority characterizing the pre-operational stage of cognitive development.
5. Socialization of the individual intelligence (the transition from the individually subjective to the social) is the main direction of cognitive development. Socialization is impossible without cooperation and collaboration, without including individuals into the actions of various “communities”.
Conventionally, the scheme of socialization of the individual intelligence, as it is presented in the theory of J. Piaget, is shown in Figure 2.
A few recent studies, conducted in the framework of the scientific school of J. Piaget, focuse on the perspective that the scholar had on the isomorphism of operational structures and structures of cooperation. Thus, in the last few years there has been an increasing interest for the issue, whether social interaction stems from some form of assistance that could precede cooperation and influence the development of thinking, and whether this kind of assistance (“co-action”) could be regarded as a source both of social and cognitive development, the de- temining condition for which it could possibly be?
Recognition of this provision would mean that the social environment affects the child’s development from the moment of birth. Moreover, recent data allow researchers to argue that the social factor plays the leading role in the emergence of a child’s ability to act consciously, to consider communicative actions as special forms of social interactions. A special analysis of communicative interactions at an early age made it possible, in particular, to say that “just as a child’s visual acquaintance with the details of the environment arises within the innate orientational movements, a smile manifests itself as a specific element of its innate communicative activity. Mothers are sensitive to the totality of the communicative actions of the child, and not to just a smile: but even when the child cannot make the smile recognizable, his mother knows how to see his sociability” [Trevarthen, 1975, p. 452]. Recently, an increasing number of followers of the scientific school of J. Piaget have come to this conclusion [Rubin, 1974], [Trevarthen, 1975], [Turnure, 1975].
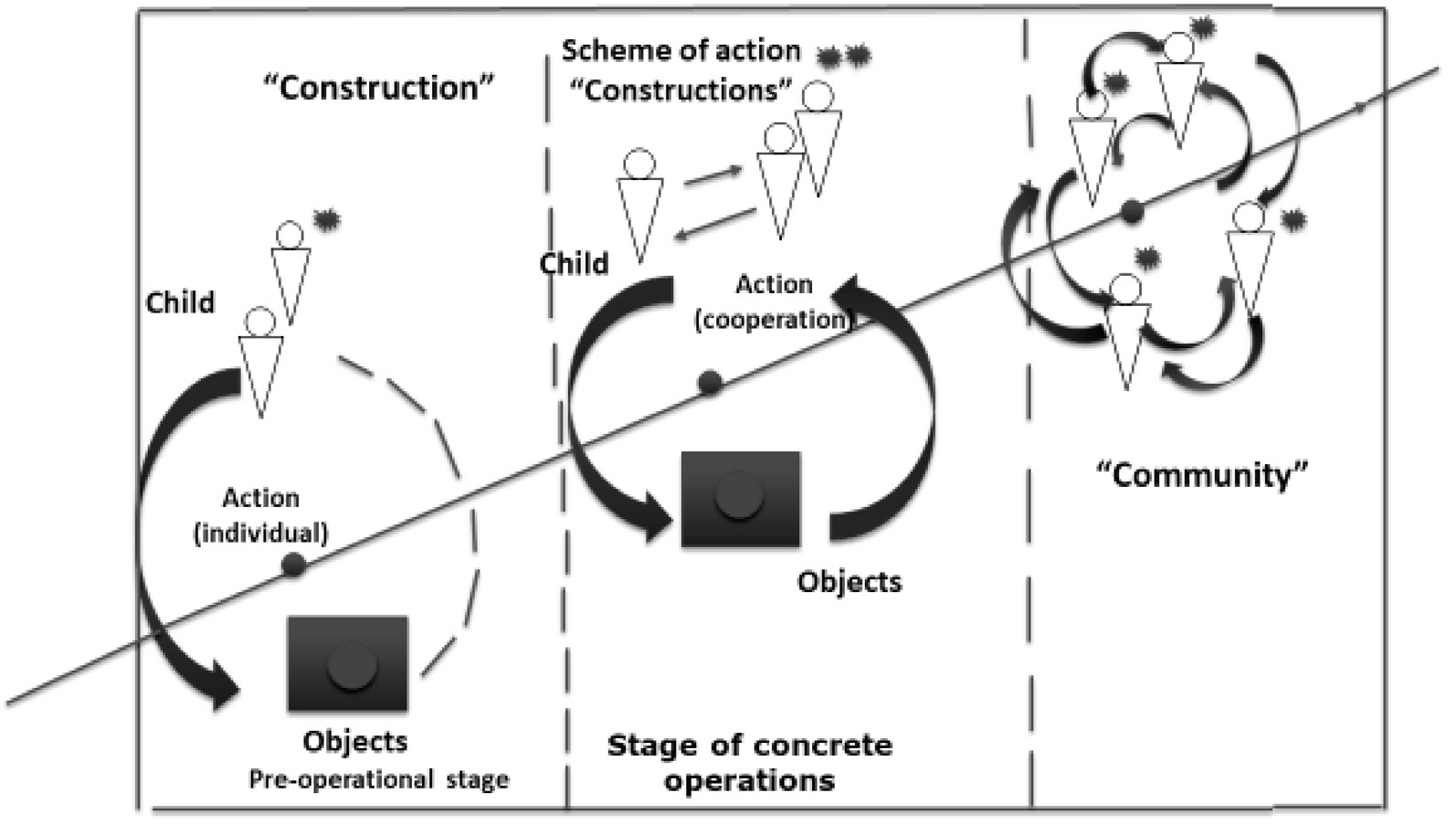
Fig. 2. Socialization of the individual intelligence (in the theory of J. Piaget)
The role of social interactions in the development of children’s thinking in the scientific school of L.S. Vygotsky. The law of development of higher mental functions. It is obvious, however, that the question of the double-facet nature (isomorphism) of intellectual structures and structures of cooperation will remain open unless the very approach to the problem of development is fundamentally revised. The foundations of this approach were laid in the scientific school of L.S. Vygotsky.
As we know, L.S. Vygotsky considered social interactions and social relations as the initial basis (source) of development. “Behind all higher mental functions and their relationships stand genetically social relationships, real relationships, homo duplex (a dual person — Latin). From here comes the principle and method of personification in the study of cultural de - velopment, that is, division of function between peo - ple, personification of functions. For example, voluntary attention — one possesses, the other one acquires. Dividing again in two what had been fused into one, experimental unfolding of a higher mental process (voluntary attention) into a small drama"1 [27, p. 1023 — emphasis added by V.R.].
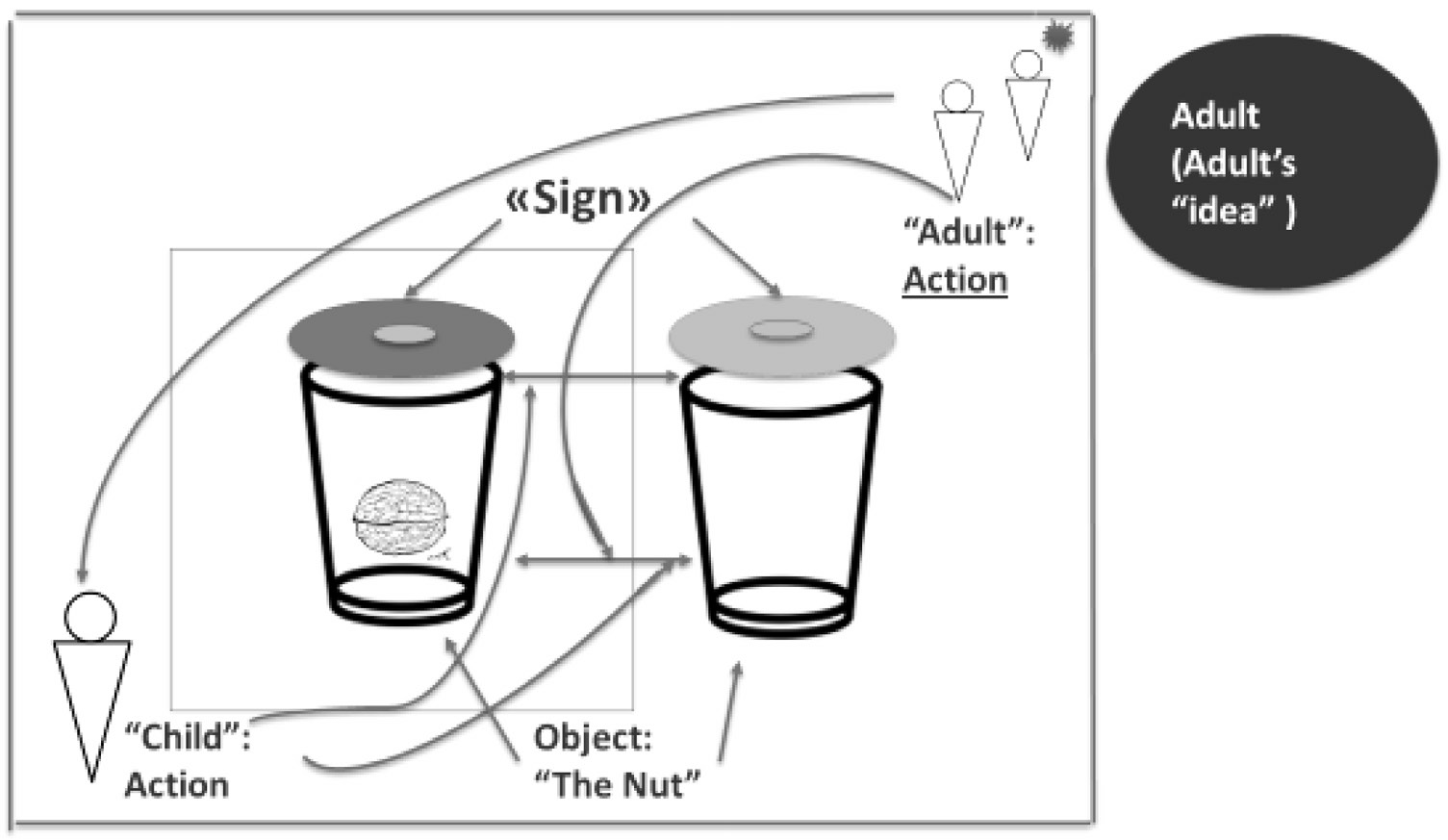
Fig. 3. Scheme of development of attention in a situation of “child — adult” interaction in L.S. Vygotsky’s experiments (the process of reflection is conventionally designated with an asterisk)
The process of mastering (acquiring) a mental function as being initially distributed between the participants of the social situation L.S. Vygotsky formulated in general terms in the well-known law of the development of higher mental functions, according to which “Every function in the child’s cultural development appears on the stage twice, that is, on two planes — first, on the social plane, and then — on the psychological plane; first, among people as an inter-psychological category, and then — within the child as an intra-psychological cat- egory”3 [Vygotsky, 1983, p. 145].
The idea of acquiring (mastering) a function as initially divided between the adult and the child was most fully implemented in the method of double stimulation developed by L.S. Vygotsky and L.S. Sakharov. This method is a prototype of the genetic modeling approach elaborated by L.S. Vygotsky for studying the development of higher mental functions. A particular technique allowed them to study in experimental settings the process of the formation of concepts as the process of meaningless words acquiring meaning, as a process of words turning into a symbol, into a representative of an object or a group of similar objects (see.: [Vygotsky, 1999], [Vygotsky, 1981]).
For L.S. Vygotsky it was essential to show that concept formation or meaning acquisition by a word is the result of a complex joint child-adult activity (that includes operating a word or a sign), in which all the basic intellectual functions are included in a peculiar combination. Thus, individual consciousness represents a product of the internalization of this activity. «... The transition (from interpsychic functions to intrapsychic ones, that is, from the forms of a child’s social collective activity to their individual functions — added by V.R.) is a common law ... for the development of all higher mental functions that primarily emerge as forms of activity in cooperation and only then are transferred by the child into the area of their psychological forms of activity.... It is not gradual socialization, which is introduced into the child from the outside, but the gradual individualization, emerging on the basis of the child’s internal sociality, that is the main path of the child’s development”4 [28, p. 343—344, emphasis by V.R.].
Learning and development in the context of social interactions: challenges that L.S. Vygotsky brought up. The stages of the development of individual consciousness from the forms of collective-social activity, indicated by L.S. Vygotsky, were precisely described by V.V. Davydov (Fig. 4). The individualization of consciousness, in the interpretation of V.V. Davydov, represents a culturally significant result of mastering of initially collectivesocial forms of activity. In this process signs and symbols act as necessary cultural means of organizing individual human consciousness.
Analyzing L.S. Vygotsky’s approach to the role of social interactions in human development, V.V. Davydov identified six main issues, brought up by L.S. Vygotsky’s scientific school. A more detailed analysis of these fundamentals allows to understsnd more deeply the nature of the development of higher mental functions [Davydov, 1998].
So, according to V.V. Davydov:
1. The basis for the development of a human being is represented by a qualitative change in their social situation or, in A.A. Leontiev’s terms, a change in human activity.
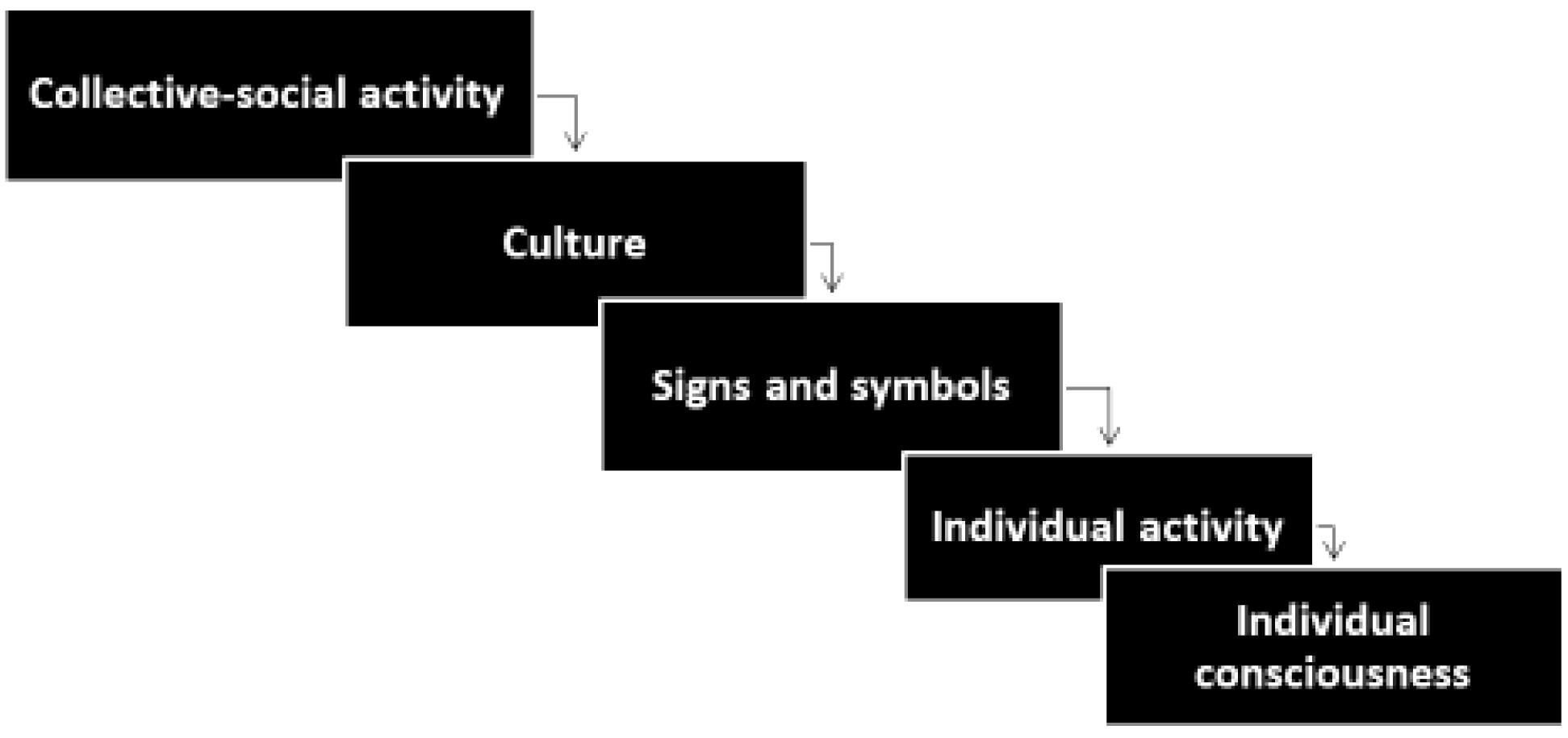
Fig. 4. Stages of development of individual consciousness from the forms of collective-social activity (according to V.V. Davydov)
2. Universal aspects of human mental development are their learning and education [“obutchenije” and “vospitanije”] (according to L.S. Vygotsky, “education [“vospitanije”] is valuable while it is ahead of development”).
3. The initial form of activity is its full-form execution by the person on the outer — social, or collective — plane.
4. Psychological neoformations (new formations), which emerge in a human being, are derivative from the interiorization of the initial form of human activity.
5. Significant role in the process of interiorization belongs to different sign and symbol systems.
6. An important part in the activity of human consciousness belongs to the internal unity of intelligence and emotions.
Socio-genetic method of research of development. The provisions, that constitute the basis of L.S.Vygotsky’s Cultural-Historical Scientific school, are indicated by V.V. Davydov as unsolved problems of the Activity Theory, and allow to investigate the mechanisms of the development of thinking in a new way, connecting these mechanisms to qualitative changes in the social situation, which are determined by changes of the forms of joint collective activity. While designing such kind of developmental settings, it is important to take into consideration the following:
1. The study of social interactions and the process of mastering (acquiring) concepts cannot be reduced to studying them simply as parallel processes.
2. Method of experimental research of the process of concept formation should be socio-genetic (compare with L.S. Vygotsky’s “genetic modeling method”). This method underlies the principle of mutual mediation of subject structures and structures of joint activity: the subject content of the object, which determines the content of the concepts acquired, is mediated by the means of interaction of the participants of social situation.
3. The organization of child-adult and child-child interactions is a necessary condition for the implementation of joint actions, since interactions and relationships of the participants determine their understanding of the relationships between various actions with the object, the properties of the object’s structure and relevant concepts.
4. The method of joint actions, which corresponds to the system of the concepts acquired, characterizes the basic didactic unit that defines the requirements for organizing the social situation.
5. It is necessary to specifically explore and design social situations, based on mediation of the object’s subject content by the means of interaction of its participants; it is also necessary to analyze the emerging child-adult communities and joint forms of activity, considerimg them as the initial forms of origin and development of emotional- semantic and symbolic-semantic structures that determine the process of mastering of the system of concepts.
It is important to highlight that socio-genetic method is grounded in the fundamental principles of the Cultural-Historical Scientific school, according to which the relationships and interactions of participants of a social situation determine the conditions for the development of child-adult communities (“obstchnost”)[Leontiev, 1994] and the corresponding forms of joint activity (see [Rubtsov, 1994], [Rubtsov, 2018]).
Numerous studies based on this method, apply a system of techniques, which made it possible to obtain new data on the impact of social child-adult and child-child interactions on the development of children’s thinking as well as to prove that these relationships influence the success of education (see [Gromyko, 1985], [Martin, 1983], [Rubtsov], [Rubtsov, a]). In particular, it was found that emerging child-adult communities are characterized by:
• the distribution of initial actions and operations (determined by a group of transformations that provide participants’ search for a general means of constructing the object under study);
• the exchange of means of action (determined by the necessity to include individual actions in new means of interaction);
• communication; distribution and exchange of actions are impossible without communication; it is due to communication that participants plan (design) the conditions, adequate for the realization of activity, and seek for joint means of activity;
• mutual understanding, conditioned by the necessity to include individual means of the participants’ action into a joint activity (allows to establish the ratio of the possibilities of one’s own actions and actions of other participants in the activity);
• reflection, which underlies the participant’s attitude to their own action (limitations and opportunities), which determines the boundaries for transformation of this action, and which is the basis for initiatiating (modelling) the search of new forms of interaction and cooperation.
Moreover, the results of recent studies, obtained by applying the developed method, have confirmed the fact that the interconnection between communication, mutual understanding and means of interaction may be perceived as an integral indicator of children’s inclusion into the joint means of problem-solving and, therefore, as a substantive feature of the emerging communities (“obstchnost”), which determines the new framework of the possibilities of development of higher mental functions in children [Rubtsov, 2018], [Rubtsov, 2008]. The analysis of the recently collected data allowed to identify 4 types of communities (“obstchnost”) [Rubtsov, 2020]:
• pre-cooperative — there is no interaction between participants; children are not involved in the joint search for a means of solving the problem;
• pseudo-cooperative — interaction between participants is substituted by actions of one of the participants; in some cases, the task is solved by one participant (individually);
• cooperative (organizational) — the emerging joint action relies on the interaction of participants, based on simple cooperation of the operations performed; children search for the solution of the problem relying on the possibilities of individual actions without analyzing the means of interaction itself;
• meta-cooperative (reflective-analytical) — the subject of the participants’ analysis is the means of interaction itself, which makes it possible to transform the means and solve the problem. The problem is solved due to the inclusion of individual actions into the joint action and exchange of actions.
Thus, the community, where children are included into the joint process of problem-solving on the basis of collaboration and cooperation, mainly differs from other possible forms of uniting the participants, in the fact that the participants are focused (oriented) on the means of interaction itself. Characteristic traits of this type of orientation in children are revealed in a targeted search for a joint means of problem-solving, which is expressed in assessing the limitations of their own actions and the actions of the other, in joint talking through and conventional illustrating (designating) scenarios of possible interactions that can be effective for problem-solving, and in the subsequent modeling (gaming) of such interactions [Rubtsov, 2018], [Rubtsov, 2020a].
In the conditions of a meta-cooperative (reflective- analytical) type of community, that has been indicated on the basis of research, the aim of communication consists in the participants’ discussion of the very possibilities of including individual actions into a joint action. In this type of community, the search for a correct solution of a problem by the participants is transformed into the task of interaction and determines a joint means of solution. Mutual understanding is mediated by the search for a means of interaction, based on the understanding of the possibilities of individual actions in a joint action. The inclusion of individual actions into a joint action becomes the main goal of interaction for these participants. Due to this, prerequisites are created for the development of new relationships and, as a result, for the emergence of a new social situation with different goals and objectives.
Data also shows that in the cooperative (organizational) type of community that has been indicated, the participants’ understanding of the possibilities of individual actions and exchange of actions is connected with problem-solving. However, the emerging communication is not oriented at a joint search for the very means of solving the problem, and the analysis of the means of interaction does not become the goal of joint action for these children. In this type of community, it is important for participants to solve the problem, rather than to figure out how to organize the interaction between themselves.
In general, our data confirms once more the idea that, on the one hand, social interactions determine the mechanism of the division of functions, and, on the other hand, the means how they are acquired (mastered). This means that the participants’ social interactions and social relationships, which initially serve as a necessary condition for the social realization of the processes of thinking and communication, later on begin to play the role of the cognitive function of self-regulation and of mental representation of certain information. These interactions activate cognitive functions that are not yet developed, which allows children to act at a higher cognitive level. Thus, a special mechanism of development in a social situation — the emotional-semantic (affective-semantic) conflict — can be indicated, that arises in the context of interactions and relationships of the participants of the social situation.
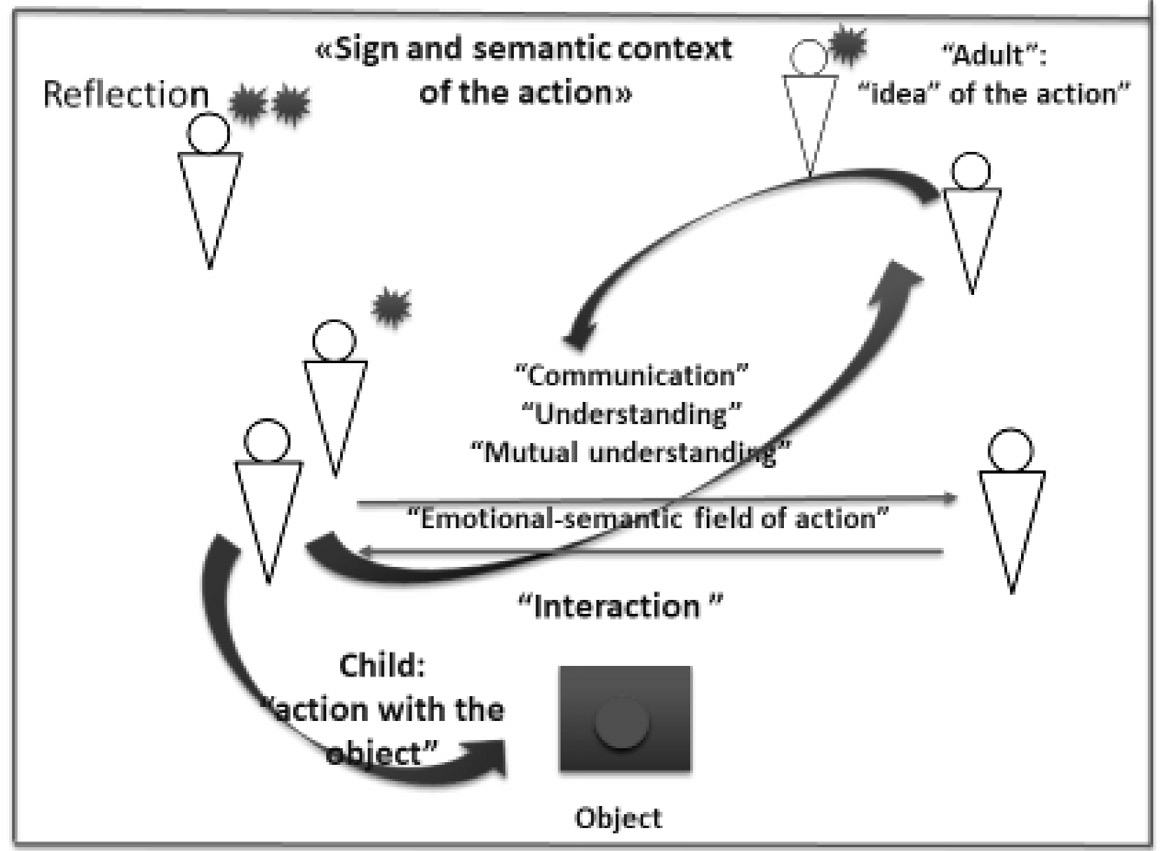
Fig. 5. Emotional-semantic (affective-semantic) conflict as a mechanism for changing the social situation
Figure 5 shows a diagram of child—adult social interactions, contributing to the emergence of an emotional- semantic (affective-semantic) conflict, which determines a change in the social situation due to the emergence of new motives and goals of the participants of the social situation. This type of interaction indicates fundamentally different conditions for the origin of thought than those denoted in the socio-cognitive conflict described in the theory of J. Piaget. It also emphasizes the originally social nature of the development of higher mental functions.
The data received allows us to discuss the question of sources of development in a fundamentally new way, based on the affective-semantic (emotional-semantic) conflict. First, there are strong grounds to believe that the change in the subject of the problem that occurs in social interactions creates prerequisites for changing the subject of the action. This change is associated with the emergence of a fundamentally new task for children to search for the very means of action. The need to solve it launches a new motivation that encourages children to organize joint actions and to search for a solution jointly. Following this motivation, participants discuss emerging constraints and design the necessary exchanges, strengthening communication and modeling means of possible interactions.
A shared emotional-semantic (affective-semantci) field, based on the participants’ experience of new opportunities and understanding of the sense of actions that they perform, emerges in these conditions. As is known, the special role of the experience (“perezhivanije”), emerging in the development of activity, was particu - larly emphasized by A.N. Leontyev, who wrote: “These forms of experience [pereghivanije] are the forms of reflection of the agent’s attitude to the motive <...> This conscious attitude of the agent of the action to its motive is the meaning of the action; the form of experience (becoming aware) of the meaning of an action is the awareness of its goal ... A change in the meaning of an action is always a change in its motivation”[Martin, 1983] [5, p. ДБ- ДО]. The results of research also testify that a change in activity in a social situation, based on the emotional- semantic conflict, occurs due to the emergence of new meanings and new attitudes to the fulfillment of one’s own actions and actions of the other participants. This happens through “perezhivanije” (experiencing) of these meanings, understanding them and sharing mutual understanding. The latter becomes a prerequisite for the emergence of new motives for activity in children. With the emergence of a new motivation, new goals and opportunities appear for the child and, therefore, new boundaries for individual actions in the context of interaction with others, appear. Children begin to jointly (together) plan new scenarios, and achieve meaningful agreement on the real interactions, as well as to design new means of joint work.
In general, the data obtained, shed a new light on the role of social interactions and social relationships in the development of children in learning, and allows to face the problem of designing educational environments as spaces of developing child-adult communities and, essentially, to redefine the requirements for a contemporary school.
The school that teaches to think: “school of L.S. Vygotsky” vs “school of J. Piaget”. The analysis of the problem of learning and development in the context of social interactions, presented in two major scientific theories of L.S. Vygotsky and J. Piaget, allows us to discuss in a very general way the issue of an effective model of contemporary school as the school of development. This discussion is based on the views that the two prominent scholars had on the sources and mechanisms of human development, particularly, on the idea that actions with objects and social interactions are interconnected — these are not parallel processes, but a means (way) of transferring knowledge and concepts mediated by forms of joint- ly-collective activity. At the same time, it is legitimate to speak both of similarities and differences in the scholars’ approaches. “Piaget’s School” of action and space for acquiring various forms of experience is to some extent alternative to “Vygotsky’s School”, based on developing forms of child-adult communities and types of activity. In general terms, the difference is reflected in the following conditional characteristics of the models of both school types.
1. The school that “teaches to think” (some definitions from the project “School of J. Piaget”):
• School of action (space for active transformation and construction).
• School of acquiring various forms of experience (exercise — physical experience — logical and mathematical experience).
• School of development of intelligence (forms of intellectual activity), which ensures the process of decentration of children’s thought and the formation of intellectual structures (schemes / models / groupings).
• School of social experience, based on role exchanges and children’s cooperation in solving problems and tasks (starting from the level of concrete operations).
2. The school that “teaches to think” (some definitions from the project “Vygotsky’s School”):
• School based on developing forms of child-adult communities and activities.
• School for implementation of age-related opportunities and development of motivation (“school of ages”).
• School based on contemporary (cultural) means of organizing communication and activities (subjectcontent environment, “smart digital environment”, etc.).
• School of the development of abilities for
— interaction and cooperation;
— communication and understanding (mutual understanding).
• School that ensures the development of reflective forms of consciousness (from social-collective to individual through the formation of sign-semantic contexts).
The requirements for the models of two types of schools, presented in the broadest possible terms, are based on the fundamentals of the two leading theories of human development, and should be taken into account while designing educational spaces and creating effective means of organizing joint activities of children and adults, and, as a result, while organizing motivating child-adult communities that promote children’s development in the process of learning [Gromyko, 2020], [Rubtsov, 1996].
[Davydov, 1998] A well-known Russian psychologist L.F. Obukhova undertook a thorough analysis of the main principles of the theory of J. Piaget (see e.g. [Obukhova, 2001], [Obukhova, 1981]).
[Leontiev, 1994] In Cultural-Historical Theory and Activity Approach by L.S. Vygotsky, A.R. Luria and A.N. Leontiev a special notion is used - “obstchnost”, which designates a particular kind of socio-emotional unity of the participants of the social situation. The closest equivalent of this concept in English is “community”, that is used in this paper.
[Martin, 1983] Translated by V.V. Rubtsov.